The 13 Most Common Side Hustle Categories (and How They Compare)
A framework and a visual heatmap to compare capital, complexity, risk, and scalability
When you search for “best side hustles,” you’ll usually find giant lists with 50 or even 100 random ideas. They’re inspiring, but not very helpful: there’s no structure, no way to compare one hustle against another.
This article takes a different approach. Instead of listing dozens of disconnected ideas, we group them into 13 categories that cover the entire side hustle landscape. And rather than treating them equally, we evaluate each one using a 7-factor framework we use at The Morning Business:
Revenue potential: how much money you can realistically make.
Startup costs: both upfront and recurring.
Operating margins: what’s left after costs.
Time to first dollar: speed to early earnings.
Reputation weight: how much credibility matters to get started.
Risk and sustainability: odds of failure, volatility, long-term stability.
Market diffusion and trend: how many people are doing it and whether the trend is rising or falling.
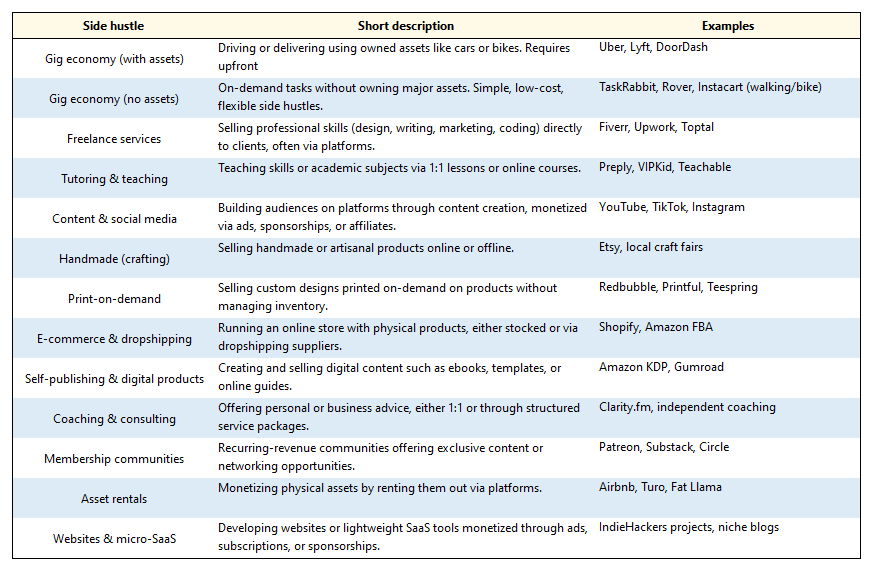
13 Side Hustle Categories
💡 This article is part of Side Hustles & Businesses — a series of practical guides to help you start and grow your next project.
If you’re reading this, you might also want to check out:
✉️ Subscribe to the newsletter to stay updated on what’s working in digital business.
1. Gig economy (with assets)
Revenues and monetization model: Earnings come from per-mile or per-delivery payments, with income directly tied to hours and demand.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Vehicle costs (fuel, insurance, maintenance) are significant; platform fees can take 15–30%.
Operating margins: Margins are thin because variable costs scale with activity.
Time to first dollar: Very fast—drivers can earn within days of onboarding.
Reputation and credibility factor: Ratings matter; poor service lowers future opportunities.
Risk and sustainability: Moderate—demand fluctuates, and high vehicle wear can erode earnings.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Highly saturated but still growing in many cities; competition pushes down profitability.
2. Gig economy (no assets)
Revenues and monetization model: Paid per task or per hour, from errands to dog walking.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Almost zero upfront costs; only platform fees apply.
Operating margins: High per hour since there are no asset costs, but capped overall by low ticket size.
Time to first dollar: Same week—often within days after sign-up.
Reputation and credibility factor: Good reviews drive repeat gigs; trust is key.
Risk and sustainability: Low—demand is steady, but earnings remain limited.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Growing, but fragmented across apps and very localized.
3. Freelance services
Revenues and monetization model: Hourly or project fees for specialized work (design, writing, coding).
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Low fixed costs, mostly software and platform fees.
Operating margins: Very high (70–90%), since costs are minimal.
Time to first dollar: Quick if you already have a portfolio; otherwise, weeks to land first clients.
Reputation and credibility factor: Crucial—portfolio, reviews, and word of mouth drive growth.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—income depends on client pipeline; economic cycles impact demand.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Highly competitive, but demand for digital freelancers is rising globally.
4. Tutoring & teaching
Revenues and monetization model: Fees per hour or per course; can evolve into course sales.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Minimal—video tools, course platforms.
Operating margins: High (70–90%), especially once courses are recorded.
Time to first dollar: Days for 1:1 tutoring; months for a full digital course.
Reputation and credibility factor: Expertise and credentials are important, especially for premium pricing.
Risk and sustainability: Low to moderate—consistent demand but subject to seasonal cycles (school terms).
Market diffusion and trend direction: Growing with online learning; niches like language and coding are hot.
5. Content & social media channels
Revenues and monetization model: Ads, sponsorships, affiliates, and digital products once scale is reached.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Basic equipment upfront; distribution is platform-dependent.
Operating margins: Very high once monetized, but near zero at the start.
Time to first dollar: Long—months or years to build enough reach.
Reputation and credibility factor: Personality and consistency are everything; audience trust is the asset.
Risk and sustainability: Medium-high—algorithms and platform policy shifts can threaten growth.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Exploding creator economy, but extremely crowded and competitive.
6. Handmade (crafting)
Revenues and monetization model: Selling physical goods at fairs or online marketplaces.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Materials and time-intensive; platform or fair fees add cost.
Operating margins: Moderate (30–60%), but manual production limits profits.
Time to first dollar: Weeks, after producing stock and listings.
Reputation and credibility factor: Reviews and quality perception drive repeat buyers.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—niche products can sell, but low volume limits growth.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Still thriving on Etsy, though competition from mass-producers is rising.
7. Print-on-demand
Revenues and monetization model: Earn per sale on t-shirts, posters, mugs; production is outsourced.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Very low startup, but marketing and platform fees reduce net.
Operating margins: Low (10–30%), unless volumes are high.
Time to first dollar: Weeks if you can drive initial traffic.
Reputation and credibility factor: Creative designs and niche targeting build credibility.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—oversaturation makes it hard to stand out.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Mature market, but still attractive for niche plays.
8. E-commerce & dropshipping
Revenues and monetization model: Product sales via online stores; profits depend on volume and ads.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Ads, shipping, supplier costs—capital-intensive compared to POD.
Operating margins: Moderate (15–40%); ad costs often eat margins.
Time to first dollar: Weeks to months, depending on sourcing and store setup.
Reputation and credibility factor: Customer trust and service are critical for repeat buyers.
Risk and sustainability: High—unsold inventory or ad misfires can wipe out capital.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Huge global market, but entry is highly competitive.
9. Self-publishing & digital products
Revenues and monetization model: Royalties from ebooks, course sales, or template packs.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Low, limited to creation and platform fees.
Operating margins: Very high (70–90%) once the product is finished.
Time to first dollar: Weeks for ebooks; months for courses or larger projects.
Reputation and credibility factor: Strong brand or expertise accelerates traction.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—success depends heavily on distribution.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Growing, especially in niches like business education and creator tools.
10. Coaching, consulting & productized services
Revenues and monetization model: High-value hourly fees or packaged services.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Very low—mostly marketing or small tools.
Operating margins: Extremely high (70–90%) since services are personal expertise.
Time to first dollar: Weeks, if network and credibility already exist.
Reputation and credibility factor: Central—clients buy trust and expertise.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—income fluctuates with client pipeline.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Rising, especially in niches like career coaching or business consulting.
11. Membership communities
Revenues and monetization model: Recurring subscription fees from members.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Platform fees (Patreon, Substack) and content/community management.
Operating margins: High (50–80%) once churn is managed.
Time to first dollar: Weeks, after setup and initial content push.
Reputation and credibility factor: Authority and trust with the niche audience are vital.
Risk and sustainability: Medium—depends on consistent value and avoiding churn.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Growing as people seek smaller, curated communities.
12. Asset rentals
Revenues and monetization model: Renting out homes, cars, or equipment.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: High—buying assets and maintaining them is capital-intensive.
Operating margins: Moderate to high (40–60%), depending on utilization.
Time to first dollar: Weeks to list, depending on approvals.
Reputation and credibility factor: Reviews are critical; trust drives bookings.
Risk and sustainability: Medium-high—accidents, regulation, or low demand affect returns.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Strong growth post-pandemic, especially in travel-related rentals.
13. Websites & micro-SaaS
Revenues and monetization model: Ads, subscriptions, sponsorships, or SaaS fees.
Costs – setup, variable, and distribution: Development, hosting, and marketing are the big costs.
Operating margins: High (60–80%) at scale; low in early stages.
Time to first dollar: Months, due to product build and distribution needs.
Reputation and credibility factor: Niche authority and user trust drive adoption.
Risk and sustainability: High—most projects fail without distribution or product-market fit.
Market diffusion and trend direction: Exploding indie hacker space, but success rates are low.
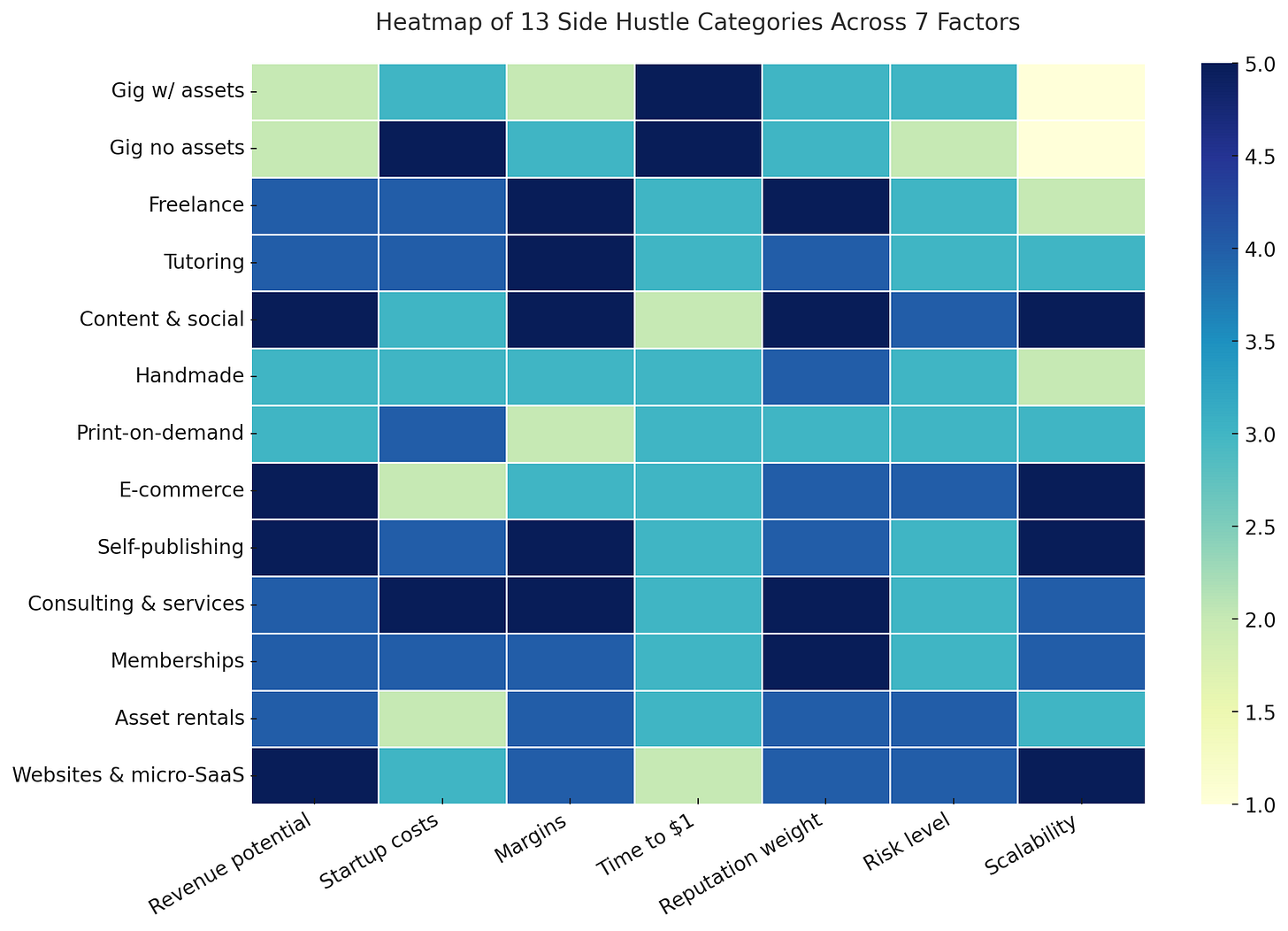
The side hustles heatpmap
To make this comparison clearer, we’ve also created a heatmap. It visualizes at a glance how each side hustle type scores across these seven dimensions, making it easier to see which models are light and flexible, and which are heavier but more scalable.
The heatmap below is built on a 1–5 scoring system for each factor:
1 = very light or low requirement (e.g. almost no capital to start)
5 = heavy or high requirement (e.g. large upfront investment, high risk, or complex operations)
Lighter colors indicate easier entry, while darker shades highlight higher requirements or risks. This visualization gives you a quick, intuitive way to compare categories before diving into the detailed breakdowns.
FAQ: Choosing and Comparing Side Hustles
What is the most profitable side hustle? Content channels, digital products, and websites or micro-SaaS typically have the highest scalability. They require time and consistency but can grow far beyond hourly work.
Which side hustle is easiest to start with little money? Gig apps, tutoring, or freelancing. They need almost no upfront capital, only your time and a basic setup.
How long does it take to earn from a side hustle? Gig apps and freelancing can generate income within days. Content, e-commerce, or SaaS usually take months before the first real dollar arrives.
What’s the safest side hustle with low risk? Tutoring and freelancing tend to be lower-risk because demand is steady and upfront costs are minimal. The tradeoff is limited scalability.
Which side hustles are best if I have a full-time job? Self-publishing, print-on-demand, and digital products work well because they can run passively once launched. Membership communities are also manageable if you dedicate fixed hours each week.
What are common mistakes people make? Chasing trends without understanding the economics. For example, starting dropshipping without enough capital for ads or misjudging how slow content growth can be. Another mistake is ignoring distribution—many projects fail not because the product is bad, but because no one sees it.